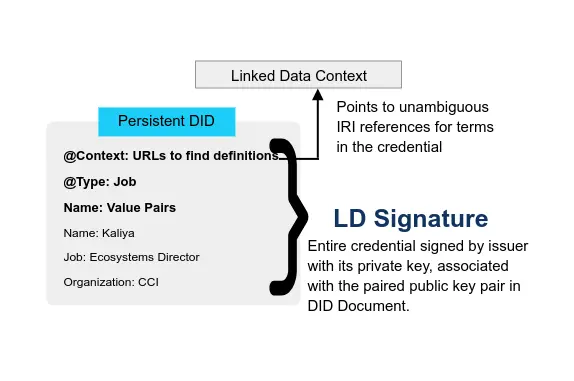
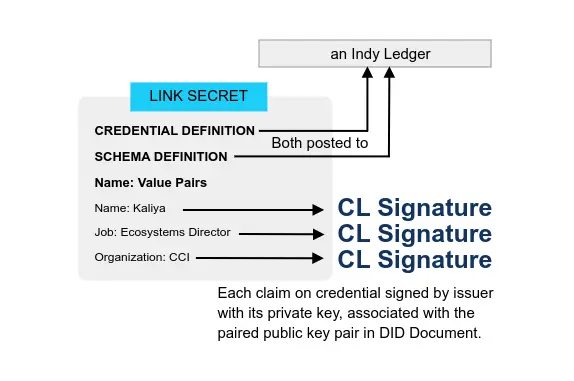
History (2015-2019) Emergence of Blockchain for Identity and the United Nations
UN Agenda for Sustainable Development

The same month, the UN unveiled it’s Agenda for Sustainable Development:
- Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels
- Substantially reduce corruption and bribery in all their forms Develop effective, accountable and transparent institutions at all levels
- By 2030, provide legal identity for all, including birth registration
- Ensure public access to information and protect fundamental freedoms, in accordance with national legislation and international agreements—(emphasis mine)
- DIGITAL IDENTITY AS A BASIC HUMAN RIGHT
- AID:Tech [T] — “is a voucher and digital identity solution for refugees. A digital record of a person’s identity is stored on a smart card, along with various additional information. Blockchain technology is used to distribute all resources in a highly traceable manner.” (another early example of blockchain for humanitarian aide)
- World Bank - Digital IDs for Development
- Additional Info on Blockchain and the United Nations
- Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development The High-level Political Forum on Sustainable Development is the central UN platform for the follow-up and review of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development adopted at the United Nations Sustainable Development Summit on 25 September 2015.
This Agenda is a plan of action for people, planet and prosperity. It also seeks to strengthen universal peace in larger freedom. We recognise that eradicating poverty in all its forms and dimensions, including extreme poverty, is the greatest global challenge and an indispensable requirement for sustainable development. All countries and all stakeholders, acting in collaborative partnership, will implement this plan. We are resolved to free the human race from the tyranny of poverty and want and to heal and secure our planet. We are determined to take the bold and transformative steps which are urgently needed to shift the world onto a sustainable and resilient path. As we embark on this collective journey, we pledge that no one will be left behind. The 17 Sustainable Development Goals and 169 targets which we are announcing today demonstrate the scale and ambition of this new universal Agenda. They seek to build on the Millennium Development Goals and complete what these did not achieve. They seek to realize the human rights of all and to achieve gender equality and the empowerment of all women and girls. They are integrated and indivisible and balance the three dimensions of sustainable development: the economic, social and environmental.
Bitcoin
9\15 Bitnation “seeks to establish the concept of ‘world citizenship’ via a bitcoin based identity, offering ‘Blockchain Emergency IDs’ to refugees. [>]
- Bitnation Pangea
- refugees.bitnation.co/
-
Andreas Antonopoulos: The Case Against Reputation and Identity Systems
Andreas Antonopoulos thinks that the key is to hedge against default risk with the blockchain instead of creating reputation systems.
-
XDI Blockstore BIP32
Historically, XDI infrastructure began by using a centralized registry model. Since this was independent of DNS and had its own commercial component, this infrastructure has been subject to criticism by various communities. After this model collapsed in late 2014, the non-profit XDI.org formed a group called the XDI Registry Working Group to begin developing a distributed blockchain-based solution. Initially, we built a PoC based on simple OP_RETURN Bitcoin transactions, where given an XDI name, its corresponding XDI number and XDI endpoint can be looked up.
Rebooting the Web of Trust
The first Rebooting Web of Trust(RWoT) workshop was held during November 2015; attracting the likes of Vitalik Buterin, Peter Todd, Gregory Maxwell, Joel Dietz, Christopher Allen, and Jon Callas, according to Andreas Antonopolis.
That workshop, produced 5 technical white papers:
5 WoT-usecases • Decentralized PKI • Smart Signatures • Creating a New World of Trust
-
Rebranding Web of Trust by Shannon Appelcline, Dave Crocker, Randall Farmer, and Justin Newton
The Web of Trust. It’s the buzzword for a new model of decentralized identity. However, it’s also a phrase that dates back almost twenty-five years and has been heavily overloaded with meaning during that time. The classic definition of Web of Trust derives from PGP, but the top Google results refer to a website reputation rating system created by a Finnish internet company. Meanwhile, some use it as a big tent that includes identity authentication & verification, certificate validation, and reputation assessment, while the vibrant blockchain community is also drawing new attention to the classic concept.
To build a contemporary Web of Trust, we need to better define it. To do so, we must both understand what the classic Web of Trust was and create a model for the elements of trust that are contained within a more modern definition.
-
Andreas Antonopoulos: The Case Against Reputation and Identity Systems
Andreas Antonopoulos thinks that the key is to hedge against default risk with the blockchain instead of creating reputation systems.
- Initial Rebooting the Web of Trust Design Workshop - San Francisco, CA — November 3rd to 4th, 2015
-
Satisfying Real World Use Cases
Decentralized systems that are engineered to prevent concentrating power as they grow avoid this. They can in fact increase their credibility as more users provide their assessments as input. Protocols and structures that are distributed and self-sovereign also offer significantly improved robustness, portability, and versatility than conventional centralized or escrowed processes — especially when combined with secure cryptography.
One of the first technologies to offer the advantages of decentralization emerged 25 years ago when the advent of PGP realized a Web of Trust that contained decentralized, cryptographically verified attestations of its users. Unfortunately, failures of UX design confined the spread of PGP to highly technical communities.
Today, decentralized Webs of Trust remain as important as ever. Now is the time to extend them to be usable by everyone who has access to digital networks, in particular to marginalized populations that can benefit from the technology. It is a fortunate tragedy that there is no shortage of real-life examples of the need for decentralized Webs of Trust in the world today. A large spectrum of individuals — from marginalized persons like stateless refugees and victims of human trafficking to members of the informal or unregulated economy — urgently need to participate in otherwise privileged economic and political fora, but they face technical, economic, and political barriers to entry.
The essential problem is to connect burgeoning new technological developments with unmet consumer needs, and vice-versa. In this paper, we present five use cases: from two relatively simple cases of managing selective disclosure to the most extreme case of establishing government-verifiable credentials from nothing for a stateless refugee.
-
Decentralized Web Summit 2016-06-09 Lightning Talks
Rebooting the Web of Trust - Christopher Allen
- Monday was the 25th anniversary of PGP. Nobody celebrated this on twitterdom
- PGP didn’t succeed. It is barely used except for code signing.
- I started #RebootingTheWebOfTrust to change this - it’s like a hackathon for white papers
- to join #RebootingTheWebOfTrust the entry fee is posting a reading list
- we wrote white papers on “what is the web of trust,use cases,creating a distributed registry”
- this led to Self-Sovereign Identity - you are the source of your own identity
- identity is not an administrative mechanism for others to control
- this inspired a UN identity conference #ID2020
- we have a lot of white papers in progress, and a 3rd conference in Sept 2016 go to weboftrust.info
-
Decentralized Public Key Infrastructure by (alphabetical by last name) Christopher Allen, Arthur Brock, Vitalik Buterin, Jon Callas, Duke Dorje, Christian Lundkvist, Pavel Kravchenko, Jude Nelson, Drummond Reed, Markus Sabadello, Greg Slepak, Noah Thorp, and Harlan T Wood
Today’s Internet places control of online identities into the hands of third-parties. Email addresses, usernames, and website domains are borrowed or “rented” through DNS, X.509, and social networks. This results in severe usability and security challenges Internet-wide. This paper describes a possible alternate approach called decentralized public key infrastructure (DPKI), which returns control of online identities to the entities they belong to. By doing so, DPKI addresses many usability and security challenges that plague traditional public key infrastructure(PKI). DPKI has advantages at each stage of the PKI life cycle. It makes permissionless bootstrapping of online identities possible and provides for the simple creation of stronger SSL certificates. In usage, it can help “Johnny” to finally encrypt thanks to its relegation of public key management to secure decentralized datastores. Finally, it includes mechanisms to recover lost or compromised identifiers.
SSI
- Self Sovereign Identity Principles
-
Self Sovereign Identity (SSI) - decentralized-id.com
Literature associated with the Fundamentals of Self-Sovereign Identity.
-
Self-Sovereign Identity - moxytongue.com
Self-Sovereign Identity must emit directly from an individual human life, and not from within an administrative mechanism created by, for,…
- A technology free definition of Self Sovereign Identity
ID4D \ Worldbank
-
Identification for Development (ID4D) Global Dataset (Global ID4D…
The Global ID4D Dataset, compiled by the World Bank Group’s Identification for Development (ID4D) initiative, provides a global estimate for the number of
-
Digital IDs for Development
This two-hour session will go over the key elements of the Digital IDs for Development program and acknowledge the support of the government of France to this agenda.
- The World Citizen: Transforming Statelessness into Global Citizenship MARIANA DAHAN, JOHN EDGE - NOVEMBER 25, 2015
-
blogs.worldbank.org/team/john-edge
Social entrepreneur specializing in financial technology and digital identity, working with international organizations to develop collaborative financial and identity inclusion strategies that enable investment from the private sector, through: (i) establishing sustainable social innovation business models, (ii) enabling interaction between regulators, government and innovators, and (iii) forwarding the agenda for SDG targets 1.4 (Ensure that all men and women, in particular the poor and the vulnerable, have appropriate new technology and financial services, including microfinance) and 16.9 (By 2030, provide legal identity for all, including birth registration).
Technical interests include trusted computing, blockchain and artificial intelligence technologies, allied with the proliferation of mobile devices, which are enabling self-sovereign identity and the emergence of commons money systems.
ID2020
-
ID2020, ID4D aim to bring legal, binding, digital IDs to all world’s citizens
It was late June of 2014 when businessman John Edge was invited to a screening of a short film directed by actress Lucy Liu. “Meena” is about an 8-year-old girl sold to a brothel and forced into sex slavery for more than a decade. It’s based on a true story. “It’s horrific,” Edge says.
A panel of experts took questions afterward, including Susan Bissell, chief of child protection at international humanitarian group UNICEF. “Susan articulated that one of the biggest problems in protecting children who are at risk of sexual violence is a lack of birth certificates or identity,” Edge says.
-
ID2020 - Digital Identity Alliance
The ID2020 Alliance is a global partnership maximizing the potential of digital ID to improve lives.
- ID2020 to kick start digital identity summit at UN with PwC support.
-
ID2020: Digital Identity with Blockchain - Accenture
Accenture has joined the ID2020 alliance and leverages its unique identity service platform. Learn about our digital identity with blockchain solutions.
-
Mastercard, Microsoft Join Forces to Advance Digital Identity Inno…
PURCHASE, N.Y. and REDMOND, Wash. – December 3, 2018 – Mastercard (NYSE: MA) and Microsoft (Nasdaq “MSFT” @microsoft) today announced a strategic collaboration to improve how people manage and use their digital identity. Currently, verifying your identity online is s…

- 4/16 the EU adopted the GDPR to be enacted as law May 2018.
- Projects aim for legal identity for everyone - ID2020, ID4D aim to bring legal, binding, digital IDs to all world’s citizens
ID2020 - Rebooting Web-of-Trust Design Workshop
The second RWoT workshop ran in conjunction with the UN’s ID2020 Summit in New York that May; clearly a significant time for decentralized identity:
1.1 Billion people live without an officially recognized identity — This lack of recognized identification deprives them of protection, access to services, and basic rights. ID2020 is a public-private partnership dedicated to solving the challenges of identity for these people through technology. - id2020.org
-
ID 2020 Design Workshop - eventbright.com
Our second #RebootingWebOfTrust Design Workshop on decentralized identity technologies will be held the weekend of May 21st and 22nd in New York City. This date was selected to follow an important digital identity policy event at the United Nations.
The day before, on the 20th of May, the non-profit ID 2020 is organizing a conference on digital identity, inclusion and human rights in the Trusteeship Council Room of the United Nations. The ID 2020 Summit will bring together industry leaders, NGOs, governments, and emerging technology experts to establish a global conversation resulting in working coalitions to address the problems around digital identity and suggest solutions. The two main goals of the UN summit are:
by 2020, be able to create a legally valid digital identity for every last person without an identity by 2030 to have rolled this capability out to at least 1 billion at-risk people to make them visible and restore them into society both personally and economically
-
WebOfTrustInfo/rwot2-id2020 - RWOT2 for the ID2020 UN Summit (May 2016).
-
RWoT2 - Topics & Advance Readings
1.1 Billion people live without an officially recognized identity — This lack of recognized identification deprives them of protection, access to services, and basic rights. ID2020 is a public-private partnership dedicated to solving the challenges of identity for these people through technology.
-
RWoT2 - Topics & Advance Readings
- Identity Crisis: Clear Identity through Correlation
-
Christopher Allen [info] [**slideshare] details the overarching history of internet identity standards in his germinal work (submitted to ID2020\RWoT workshop):
-
The Path to Self-Soverereign Identity[ϟ] details the history of identity standards leading up to self-sovereign and details the 10 principles of self-sovereign identity.
I am part of the team putting together the first ID2020 Summit on Digital Identity at the United Nations
-
The Path to Self-Soverereign Identity[ϟ] details the history of identity standards leading up to self-sovereign and details the 10 principles of self-sovereign identity.
Evident from the other whitepapers submitted to the second RWoT Workshop, the DID identifier had begun to emerge:
-
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) and Decentralized Identity Management (DIDM)
“Decentralized Identifiers (DID) stored in a permissioned blockchain enable principals to directly control their own identities with cryptographic proofs and secure, addressable network endpoints. DIDs further enable a Decentralized Identity Management (DIDM) infrastructure that will empower people and organizations to securely and confidentially manage and assert their identities.”
-
Requirements for DIDs
“Respect Network is conducting a research project for the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, HSHQDC-16-C-00061, to analyze the applicability of blockchain technologies to a decentralized identifier system. Our thesis is that blockchains, or more generically distributed ledgers, are a potentially powerful new tool for “identity roots” — the starting points for an Internet identity. However “blockchain identity” may not fully address the core security and privacy principles needed in a complete identity system. In this case DIDs — Decentralized Identifiers rooted on a distributed ledger — may end up being a foundational building block for higher level identity management solutions. -
- Identity System Essentials 3/16 (Original Evernym Identity WP also submitted to ID2020\RWoT workshop)
Evernym

Evernym[T] originally created the Sovrin codebase, founded in 2013.
-
Timothy Ruff (@RuffTimo)
Out of stealth mode at last: http://evernym.com #identity #privacy #fintech #me2b #FOSS
-
Evernym: Life’s Username
Privacy so strong, we patented it
Evernym literally means “forever name.” We give the control of your digital communication back to you—the receiver—not any anonymous sender who happens to have your address.
- Identity System Essentials - Samuel M. Smith Ph.D. and Dmitry Khovratovich Ph.D. - 29 March 2016
- Outlier Ventures invests in, becomes strategic partner of Evernym[ϟ]
- The Three Models of Digital Identity Relationships — How self-sovereign identity (SSI) is different, and why it’s better
- Applying Blockchain to Decentralized Identity - SBIR - Drummond Reed
Sovrin
- Sovrin Foundation Launches First Dedicated Self-Sovereign Identity Network
-
Hyperledger Welcomes Project Indy – Hyperledger
Guest post: Phillip J. Windley, Ph.D., Chair, Sovrin Foundation We’re excited to announce Indy, a new Hyperledger project for supporting independent identity on distributed ledgers. Indy provides tools, libraries, and reusable…
- Announcing the Sovrin Foundation
-
Respect Network Company Profile: Acquisition & Investors - PitchBook (Sovrin Aquisition - Respect Network)
Information on acquisition, funding, cap tables, investors, and executives for Respect Network. Use the PitchBook Platform to explore the full profile.
MyData
Humanitarian Blockchain SUmmit
-
Humanitarian Blockchain Summit - November 10th, 2017
brought experts, scholars, and humanitarian practitioners together at the United Nations Headquarters; enlarging the discussion around using blockchain technology for pursuit of the Sustainable Development Goals. At the summit, the World Identity Network (WIN), the United Nations Office for Project Services (UNOPS) and the United Nations Office of Information and Communications Technology (UN-OICT) announced a partnership to launch a pilot using blockchain to provide identification to children at risk for child trafficking.
Learning Machine \ Blockcerts
-
Verifiable Credentials on the Blockchain
The MIT Media Lab and Learning Machine have been working on a collaborative project for issuing official records to recipients, and anchoring them onto the Bitcoin blockchain. We’ve just open-sourced the first version of that project and named it Blockcerts. It allows education providers, employers, and others to issue official certificates that supply proof of membership, completion, or achievement. These certificates can be collected by individuals and shared directly with anyone who requires official documents. The Bitcoin blockchain is currently being used as the secure anchor of trust to ensure that each certificate is authentic, unchanged, and still valid.
-
Blockcerts on Github
Blockcerts is an open standard for creating, issuing, viewing, and verifying blockchain-based certificates.
The Future is Decentralized
Blockchain.com (2011) partners with ArtFinLab, UN Refugee Agency (UNHCR), the UN Development Programme (UNDP), and the World Economic Forum (WEF) - committed to supporting sustainability, humanitarian, and environmental initiatives. (3/2018)
-
The Future is Decentralised • ANN - Describes the blockchain applications being explored within the UN, at time of publicaiton.
- Dublin-based AID:Tech brings social and financial inclusion to the world’s undocumented and underserved populations by delivering digital entitlements using block chain-based digital identities. In December 2015, they teamed up with the Irish Red Cross and Lebanese humanitarian experts to test and develop a vital element of their technology in the most demanding conditions possible. They focused on Syrian war refugees in and around Tripoli in northern Lebanon, and set out to ensure that not only did the refugees receive aid, they were able to do so with improved user experience that preserved their dignity. This was the first time ever that international aid was delivered completely transparently using block chain technology.
UN/CEFACT Conference / Workshop on Blockchain April 2018
-
Security and Authentication for Blockchain
• Identity • Identification and Authentication • Authorization and Non-repudiation/ Admissibility of Electronic Evidence • Time Stamping • Data Access, Sharing, Retention, Accuracy and Integrity • Liability Issues and Dispute Settlement • Mutual Recognition
Blockchain for Impact \ AID:Tech
Blockchain For Impact Hosts Inaugural Summit at the UN on Frontier Technologies to Power the SDGs held inaugural Blockchain for Impact summit in NYC.
-
BLOCKCHAIN FOR SOCIAL IMPACT MOVING BEYOND THE HYPE
The World Bank estimates that over 1.5 billion people on the planet are unable to prove their identity.1 Many of these people come from remote, underserved regions. Using blockchain technology to build and deploy digital identity solutions, if applied correctly, holds promise because it can reduce fraud, increase transparency, and increase efficiency. Several organizations, like BanQu and AID:Tech, are already changing digital identity in the developing world with a blockchain solution, making it easier for NGOs, nonprofits, and commercial entities to provision identities, track aid, and enable underserved populations to access a wider range of economic services.
First Live Birth Recorded on Blockchain
Jun 21, 2018 - The first baby born ‘on the blockchain’ tethering the digital identity of mother and child, in partnership with PharmAccess Foundation
Aid:Tech assisted in the first birth ever to be recorded on the blockchain, with two more only days later. Partnered with PharmAccess, Aid:tech brings charitable donations to pregnant women in Tanzania, uses blockchain records to ensure the women get proper pre-natal care; and tracking the progress of their pregnancies.
Consensys
-
The Identity Crsis
Identity is defined in Merriam’s dictionary as “who someone is”. As the world and technology evolves one can’t help but notice the changes to the notion of who someone is and how this affects their relation to the world. We’ll focus on the problems that affect humans in regards to their identities, dividing the conversation into developed and developing economies.
- Identity of the Blockchain: Perils and Promise - slideshare - Christopher Allen
-
Decentralized Identity Foundation Announces Formation At Consensus 2017
The Decentralized Identity Foundation will collaborate across industries to research personal identity solutions.
-
uPort: The Wallet is the New Browser
Many people feel user-owned identity and data will be crucial for realizing the compelling vision of Web 3.0. uPort will act as a unique and user-controlled perspective on the blockchain based upon the persona(s) of the user.
Decentralized Identity Foundation - DIF
On May 22 at Consensus 2017 the formation of the Decentralized Identity Foundation (DIF) was announced:
The Decentralized Identity Foundation will collaborate across industries to research personal identity solutions.
- Conensus 2017 - Building an Foundation for Decentralized Identity (video)
- Decentralized Identity Foundation Grows To 56 Members In Our First Year
- A Universal Resolver for self-sovereign identifiers • uniresolver.io On any blockchain or other decentralized system
Verifiable Credentials

- [EDITOR’S DRAFT] Verifiable Claims Working Group Frequently Asked Questions
- Verifiable Claims Working Group Charter Approved; join the Verifiable Claims Working Group (Call for Participation
-
W3C Verifiable Claims Working Group
The mission of the Verifiable Claims Working Group is to make expressing and exchanging claims that have been verified by a third party easier and more secure on the Web.
-
OpenCreds • source
COMMUNITY: The W3C Credentials Community Group website. - opencreds/website
DID

- Requirements for DID - RWOT2 for the ID2020 UN Summit (May 2016).
- Applying Blockchain to Decentralized Identity - sbir.gov
DID Auth

IBM Blockchain
- Blockchain for Identity Management IBM part 1 of 3
- Blockchain for Identity Management IBM part 2 of 3
- Blockchain for Identity Management IBM part 3 of 3
-
Self-sovereign identity: Why blockchain? - Blockchain Pulse: IBM Blockchain
One of the most common questions I get when talking to customers and analysts about the self-sovereign identity (SSI) movement is, “Why blockchain?”
BTCR
-
BTCR DIDs and DDOs By Kim Hamilton Duffy (Learning Machine), Ryan Grant, and Christopher Allen
BTCR is a DID method that is based on the Bitcoin blockchain. The BTCR DID scheme uses a TX Ref-encoded (described below) transaction on the Bitcoin blockchain. The DID Description is constructed from a combination of the transaction details and an optional “continuation” DID Description, the address of which is stored in the OP_RETURN field. This could be a link to an IPFS address of a DID Description with additional entities.
-
BTCR DID Resolver Specification By: Kim Hamilton Duffy, Christopher Allen, Ryan Grant, Dan Pape
This describes the process of resolving a BTCR DID into a DID Document. The draft reference implementation is available at https://github.com/WebOfTrustInfo/btcr-did-tools-js (see didFormatter.js). Note that not all steps described in this document are implemented yet.
-
BTCR TX Conversion Playground
This is the BTCR DID Method playground.
World Economic Forum - 2018
- The Known Traveller Unlocking the potential of digital identity for secure and seamless travel - weforum.org
-
Identity in a Digital World: A new chapter in the social contract - weforum.org
All over the world, a growing number of organizations –from the public and private sectors –are advancing systems that establish and verify digital identities for people, devices and other entities. Yet we are still learning what “identity in a digital world”means. We…
DHS-SBIR
-
Applying Blockchain to Decentralized Identity
Respect Network will research and develop a decentralized registry and discovery service for Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) to integrate with the public blockchain. DIDs will allow principals to directly control their own identities with cryptographic proofs and secure, addressable network endpoints. DIDs will enable a Decentralized Identity Management (DIDM) infrastructure that will empower people and organizations to securely and confidentially manage and assert their identities. Open standards and established industry protocols will permit principals to selectively disclose identity claims, and to manage their privacy and digital relationships. Respect Network’s thesis is that the combination of DIDs and DIDM architecture, using public and/or private blockchains as “identity backbones”, can meet traditional information security principles of confidentiality, integrity, availability, non-repudiation and provenance. Further, our approach applies privacy-by-design principles, including user control, selective disclosure of information and pseudonymity.
-
Credentials on Public/Private Linked Ledgers
A wide variety of applications could benefit from combining identity management technology with decentralized ledgers (aka blockchains). However, not every application uses the same data or requires the same consensus or authorization models. While a single solution is unlikely, we assert each application could benefit from a standard, configurable, decentralized ledger with flexible semantics. We will study the feasibility of this concept by building a proof-of-concept Linked Data ledger format and architecture.
-
News Release: DHS S&T Awards $750K to Virginia Tech Company for Blockchain Identity Management Research and Development
DHS S&T has awarded a $749,241 Small Business Innovation Program (SBIR) contract to Digital Bazaar, Inc. to develop fit-for-purpose blockhains for identity and access management.
-
News Release: DHS S&T Awards $749K to Evernym for Decentralized Ke…
The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Science and Technology Directorate (S&T) has awarded Salt Lake City-based startup Evernym a $749,000 Small Business Innovation Program (SBIR) award to develop an easy-to-use, decentralized mechanism for managing public and private key…
DKMS - Decentralized Key Management

- A Framework for Designing Cryptographic Key Management Systems - NIST Special Publication 800-130 - 2013
Veres One
-
veres-one/veres-one - began on GitHub Jul 16, 2017
A ledger for acquiring and managing decentralized identifiers - veres-one/veres-one
-
Recent happenings with Linked Data Capabilities
Veres One’s architecture has been adjusted to take full advantage of Linked Data Capabilities as its primary mechanism for granting authority to perform operations on the ledger as well as on DID Documents. permission to update key materials can be conditionally handed out to an entity (or entities) and later revoked if deemed appropriate using Linked Data Capabilities’ design.
As for ledger updates, Accelerators also make use of Linked Data Capabilities. To prevent spamming the ledger, the costs of an update must somehow be accounted for. The traditional way to do this on a blockchain is to use proof of work, and this is also an option in Veres One, but for those use cases where expending time and energy on proof of work is less desirable users can use an “accelerator”.
An accelerator is an entity that has been granted a capability to perform updates on the ledger more quickly. Accelerators may likewise take advantage of Linked Data Capabilities’ support for delegation, with or without caveats.
ERC 725
-
ERC: Proxy Account · Issue #725 · ethereum/EIPs
eip: <to be assigned> title: ERC-725 Proxy Account author: Fabian Vogelsteller (@frozeman) <fabian@ethereum.org>, Tyler Yasaka (@tyleryasaka)
-
Introducing the ERC-725 Alliance
The ERC-725 Alliance proposes a standard for blockchain-based identity. What is ERC-725 and why is it valuable?
Microsoft
- Decentralized Identity - Own and control your identity - Microsoft Identity Whitepaper - 2018
von-bcgov
- Verifiable Organizations Network - A Production Government Deployment of Hyperledger Indy (live 9-10-18)
Digital Bazaar Global Standards for Organizational Identity
- Digital Bazaar Collaborates with GS1 US, SecureKey and TradeLens on Global Standards for Organizational Identity
-
Blockchain - A U.S. Customs and Border Protection Perspective
CBP and DHS built a system using Digital Bazaar’s Veres Delta, a software that is able to translate between entities and software regardless of the blockchain software used. The software platform enabled the government to exchange information between several different blockchain systems seamlessly. The specifications championed by DHS S&T, and now CBP, focus on Decentralized Identifiers, Verifiable Credentials, and Decentralized Key Management System. CBP has adopted these specifications as the standard for the industry to do business with our agency. It is important to note that each of these specifications have been vetted through GS1 (Global Language of Business) and W3C (Worldwide Web Consortium). Utilizing existing protocols, this system allows for an open market and true interoperability between blockchain software. This is something that has not been fully achieved by anyone else that this author is aware of.
-
NAFTA/CAFTA Proof of Concept - Overview & Results
The North American Free Trade Agreement/Central America Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA/CAFTA) proof of concept (POC) tested the application of Blockchain technology for the entry summary submission process for NAFTA/CAFTA entries. A joint effort was spearheaded by Customs and Border Protection (CBP), Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and private sector organizations. The POC specifically tested the feasibility of the technology for receiving certificate of origin (CO) data and conducting free trade agreement (FTA) origin verifications. Via the test, CBP could request information through the Blockchain to substantiate a claim in lieu of CBP Forms 28 and 29. As a result, the POC achieved almost instantaneous communications between CBP and trade, improved documentation of receipt, and expedited processing for CBP.
-
Digital Bazaar Welcomes TradeLens as Key Organizational Identity Blockchain Technology Participant: Improved Business Efficiency and Identity Security
BLACKSBURG, Va., Sept. 10, 2019 /PRNewswire/ – Digital Bazaar (https://digitalbazaar.com/) and TradeLens (https://www.tradelens.com/) recently announced a strategic collaboration to help facilitate and implement an array of digital ID solutions intended for wide use across the supply chain industry. TradeLens is a digital platform jointly developed by Maersk and IBM that empowers businesses and authorities along the supply chain with a single, secure source of shipping data. Utilizing Organizational Identity automation pioneered by Digital Bazaar, both TradeLens and Digital Bazaar are poised to improve collaboration via the use of blockchain-based secure identity proofing and data sharing technology.
-
Digital Bazaar and SecureKey Join Forces to Develop Global Standards for Organizational Identity - Secure Key and DB join forces w Verified.me in canada (toronto based, formerly DID agnostic)
BLACKSBURG, Va., Sept. 17, 2019 /PRNewswire/ – Digital Bazaar (https://digitalbazaar.com/) and SecureKey Technologies (https://securekey.com/) recently announced a strategic collaboration to leverage new digital identity standards intended to enhance existing paper-based identity verification processes. Both companies join a growing web of technology providers – including GS1 US and TradeLens – that are working together to improve data sharing and collaboration through blockchain-based approaches and innovative authorization technologies. With combined industry expertise, this project will help set the foundation for more robust global standards for interoperable organizational identity. It will also demonstrate the value of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) emerging standards around digital identity for interoperable use in business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-government (B2G) interactions.
-
Digital Bazaar and GS1 US® Collaborate on a New Proof of Concept Exploring the Intersection of Organizational Identity and Blockchain Technology
BLACKSBURG, Va., Sept. 24, 2019 /PRNewswire